









Table of
Contents
My Web Stats Until Dec 2008
| |
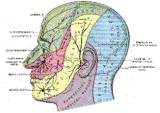
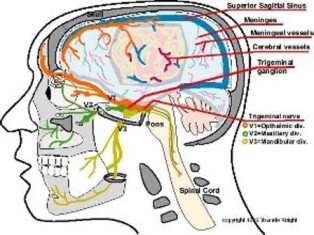
Pain-Sensitive Structures
- Intracranial
- Arteries at the base of the brain and their major branches
- Periarterial dura mater
- Venous sinuses
- All Extracranial structures
- Cranial nerves : 5,7,9,10
Pathway
Supratentorium : Trigeminal nerve
Infratentorium : Glossopharyngeal nerve, Vagus nerve, Cervical spinal root (2)
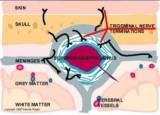
Gate-Control System
- Substantia gelatinosa
- Descending pain control system : periaqueductal gray, locus ceruleus,
medulla, dorsolateral fasciculus, dorsal horn
Neurotransmitter
PNS
- substance P
- histamine, 5-HT, bradykinin, PG
- ANS change
- Drugs : NSAIDs
CNS
- Substance P
- Inh : encephaline
- Drugs : Mo
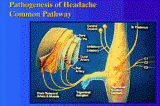
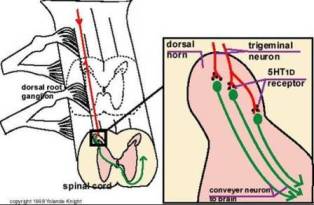
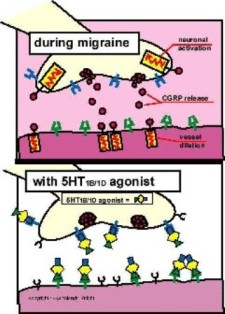
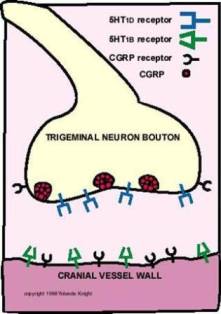
Mechanism
Organic Headache
- Traction-inflammatory headache
- Neurogenous pain
Functional Headache
- Vascular headache
- Muscke pain
- Psychogenic pain
- Multiple mechanism
Traction-Inflammatory
Pain sensitive structure
IICP, meningeal irritation
Giant cell arteritis
Neurogenous Pain
Paroxysmal neuralgia pain
May not along dermatome
Cranial neuralgia
Symptomatic or idiopathic
Demyelination of axon from compression (vv)
Neuritic Neuralgia
Along dermatome, consistent
Post-herpetic neuralgia
Inflammation, metabolic, toxic
Traumatic Neuroma
Post-trauma or Sx
Abnormal growth of extraneural, intraneural tissue and Schwann cell
Deafferentation pain
Anesthesia dolorosa, causalgia, phanthom limb
Anbnormal growth of nerve and dorsal root ganglion dysfunction
Vascular Headache
Migraine
- Neurogenic or vasculogenic
- Biochemical change
Cluster Headache
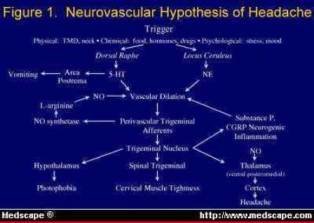
Muscular Headache
Myofascial pain
Less spasm, normal EMG
Trigger point
Muscle spasm pain
Change in proprioceptive and sensory input or CNS dysfunction
Psychogenic Pain
Migraine
Myofascial pain
Conversion, depression
Multiple Mechanism
Post-traumatic headache
Summarized By Thirayost Nimmanon
โดย ธีรยสถ์ นิมมานนท์
 
|
