|
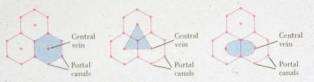
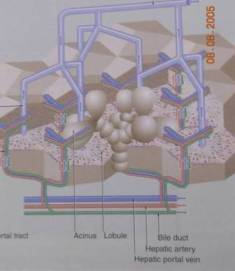
- Hepatic Acini (Rappaport)
- Portal Lobule
- Classic Lobule
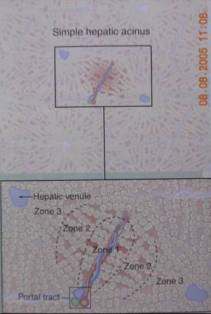
Hepatic Acini (Rappaport)
Hepatic Lobule

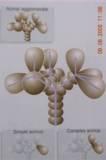
Relationshop Between Acini and Lobule
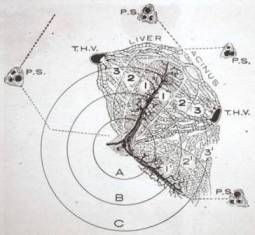
zone
1 = peripheral area
zone
2 = midzonal area
zone
3 = several centrilobular area
Back To Top of This Page
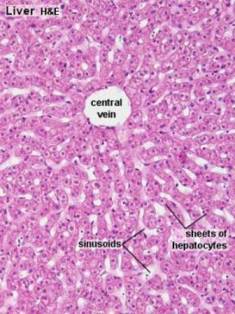
One-cell thick, sponge-like plates separated by sinusoids
Two-cell thick in children up to 5-6 years
Polygonal epithelial cell
Well defined plasma membrane
- Basolateral 75%
- Bile canalicular 15%
Hepatocytes : Nucleus
Centrally located, Round
Contains one or more nucleoli
May be binucleated, Rare mitotic activity
May be polyploid in elderly persons
Glycogen accumulation found around portal tracts in adolescent and may be
conspicuous in adult with some conditions : DM, pancreatic carcinoma, CHF (no
diagnostic significance)

Polyploid nuclei, larger than normal nuclei
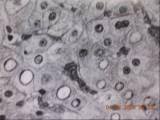
Intranuclear vacuoles found in particular conditions
Hepatocytes : Cytoplasm
Eosinophilic
Contains fine basophilic granules : RER
Fine, reticulated, foamy appearance from glycogen accumulation
Diurnal and diet-related

Intracytoplasmic glycogen accumulation
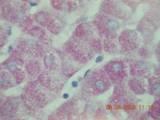
PAS staining confirming glycogen in cytoplasm of hepatocytes.
Iron-containing vacuoles
found in older individuals
Hemosiderin and copper
0-9 months old
Coarse, birefringent
Periportal hepatocytes
Lipofuscin
Wear and tear pigment
Fine, well delineated, light brown
PAS-positive, diastase-resistant, partly acid-fast positive
Zone 3 particularly at the canalicular pole
Progressive increasing
Oxidized lipids in lysosomes
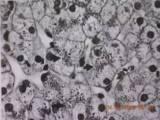
Bile
Poorly defined, less granular
Thrombi formation in canaliculi of zone3
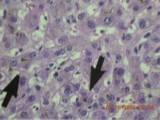
Age-Related Variation

Fetal Liver Histology
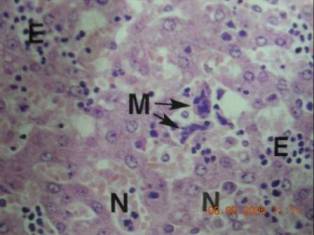
Extramedullary hematopoiesis in liver
Back To Top of This Page
Intercellular space
Apposition of the edges of gutterlike hemicanals on adjacent surfaces of 2-3
neighboring hepatocytes
Connect to small portal bile ducts via canals of Hering

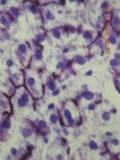
Chicken-Wire Like (enzyme histochemical method for ATPase)
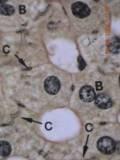
Iron Hematoxylin
Back To Top of This Page
Endothelial cells
Thin, indistinct, sievelike cytoplasm
Small, elongated, darkly stained nuclei without nucleoli
Absent basement membrane
Kupffer cells
Bean shape nucleus
Plump cytoplasm with star-shaped extensions
Near portal tract, mononuclear-phagocytic
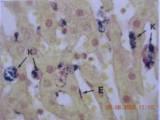
Special preparation showing endothelial cells and kupffer cells.
Space of Disse
Zone of rapid intercellular exchange
Containing
- plasma
- scant CNT : reticulin forming reticular network
- perisinusoidal cells : lipocytes/Ito and pit cells

Sinusoids and Disses Space
Lipocytes
Modified resting fibroblasts
Stores fat and vitamin A and produces collagen
Significant role in hepatic fibrogenesis
Prominent in hypervitaminosis A
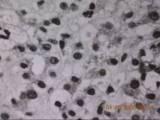
Lipocytes
Back To Top of This Page
Hepatic vein, sublobular vein, terminal hepatic venule
Determine the size of an acinus
Very thin wall lined by endothelial cells, demonstrated by Trichrome or Victoria
blue
Perivenular sclerosis in alcoholic patients : an index of progressive liver
injury
Thickening of wall of THV is found in
- Pericellular fibrosis
- Central hyaline sclerosis

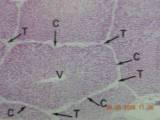
Terminal Hepatic Venule
Back To Top of This Page
Containing
- Hepatic artery branch
- Portal vein branch
- Bile duct and ductules
- Lymphatic channels
- CNT
Amount of CNT and size of intraportal structures depend on the size of the
portal tract
Autonomic nerves may be seen
Contains few lymphocytes, macrophages and mast cells
No PMN or Plasma cells
Glissons capsule extensions into parenchyma must not be interpreted as
cirrhosis in specimens of subcapsular parenchyma
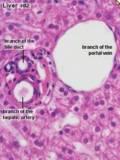
Bile Duct
Cuboid to columnar epithelial cells
Larger bile ducts are located in the central part and have more periductal
fibrous tissue
Irregular, circumferential, but not concentric, manner as in sclerosing
cholangitis and cholecystitis
Always accompanied by a portal vein and hepatic artery
Connectd to canaliculi by bile ductules and canals of Hering
Bile Ductule
Cuboid
Peripheral zone of the portal tract
Accompanied by only portal vein, not by a hepatic artery branch
Canals of Hering
Not discernible
Partly by ductular cells and partly by hepatocytes
Circulation
Limiting Plate
Very important landmark to define pathology of liver
It is destroyed in active hepatitis

Chronic Active Hepatitis
Back To Top of This Page
Liver Histology for Pathologists
Summarized By Thirayost Nimmanon
สรุปโดย ธีรยสถ์ นิมมานนท์
 
| 